Use Gitserver with partial replicas
Learn how to manage partial replicas when working with GitHub and Unity Version Control.
Read time 2 minutesLast updated 4 months ago
Unity Version Control (UVCS) supports partial replicas, which don’t map to GitHub. Avoid or work around issues in mixed GitHub and UVCS scenarios.
Partial replicas aren’t visible to GitHub
Ensure that GitHub mappings only calculate when the correct branches are in the UVCS repository. When GitServer indexes new changesets, it creates GitHub mappings. GitServer ignores any pushes that can alter the SHA of a changeset and potentially break synchronization with GitHub repositories that have already pulled a changeset. For example, the following screenshot shows that you can push changeset 10, even if changeset 9 on branch001001001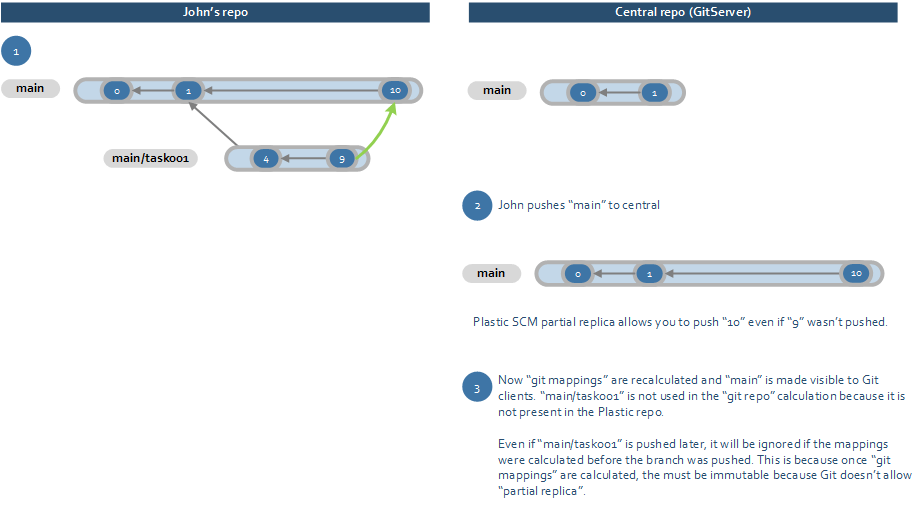
A side by side screenshot of the visual branch explorer in UVCS compared with the branch explorer for the central repository (GitServer). The screenshot has annotated text that repeats the information in the previous paragraph.
Unlinked branches aren’t visible to GitHub
Because GitHub doesn’t allow partial replicas, any branches that don’t have a parent branch that links them to themain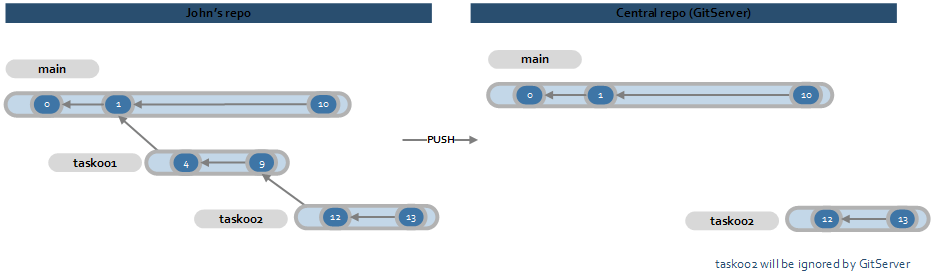
A side by side screenshot of the visual branch explorer in UVCS compared with the branch explorer for the central repository (GitServer). The screenshot shows that a branch not directly linked to main is ignored by GitServer.
mainForce map unlinked branches
To make a branch available to GitHub even if it doesn’t have a parent branch or the changesets don’t meet the required conditions, addadd branch.toForceMapgitserver.conf# branches which changesets are made visible# although they have unlinked merge sourcesbranch.toForceMap=/main
Xlinks with Gitserver
Gitserver ignores changesets with unresolved Xlinks so they aren’t visible to GitHub clients. For example, if you have a branchmain@rootmain@xlink15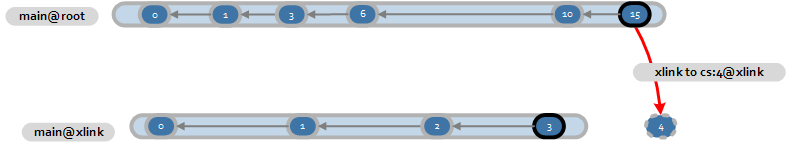
A screenshot of the visual branch explorer that shows that changeset `15` is xlinked to a changeset that isn't replicatied or linked to the main branch.
15Force GitServer to ignore missing xlinks
To configure GitServer to skip missing Xlinks and allow synchronization with GitHub even if you lose some content, addunresolvedxlink.skip=truegitserver.conf# skip the xlink entries that cannot be resolvedunresolvedxlink.skip=true