Repair meshes
Use this feature to repair meshes, mesh per mesh.
Read time 1 minuteLast updated 3 months ago
API function: algo.repairMesh We strongly recommend that you repair meshes before optimizing models. Meshes may have various issues:
- Gaps and cracks
- Z-fighting, that is, overlapping surfaces
- Non-manifold edges, that is, edges that are shared by more than two faces
- An unnecessarily high polygon count
- An increased frame rate
- Delete duplicate polygons.
- Repair connectivity:
- Merge vertices that are closer than the specified tolerance. Read more.
- Fix T-junctions and sew boundaries that are closer than the specified tolerance.
- Delete degenerate polygons. Read more.
- Optionally, crack non-manifold surface edges, that is, split them into two or more manifold edges, if possible.
- Optionally, flip adjacent faces consistently to the same side.
Duplicate polygons
Duplicate polygons overlap. Their vertices coincide but aren't connected. As a result, the polygon count may be unnecessarily high. Visual artifacts, such as Z-fighting, may affect the mesh quality. This feature maintains only one polygon.T-junctions
This feature sews the boundaries of the selected meshes even if the vertices don't coincide.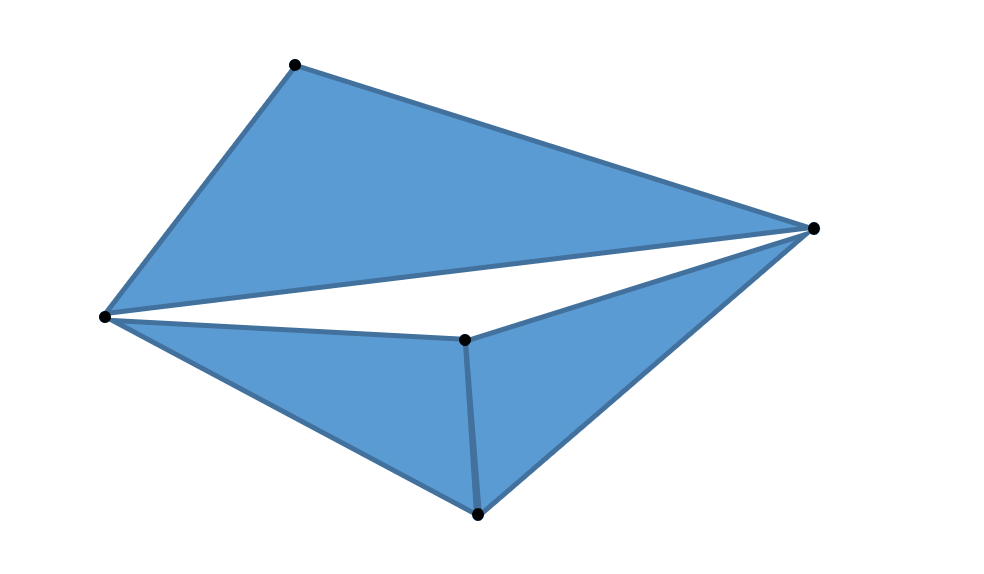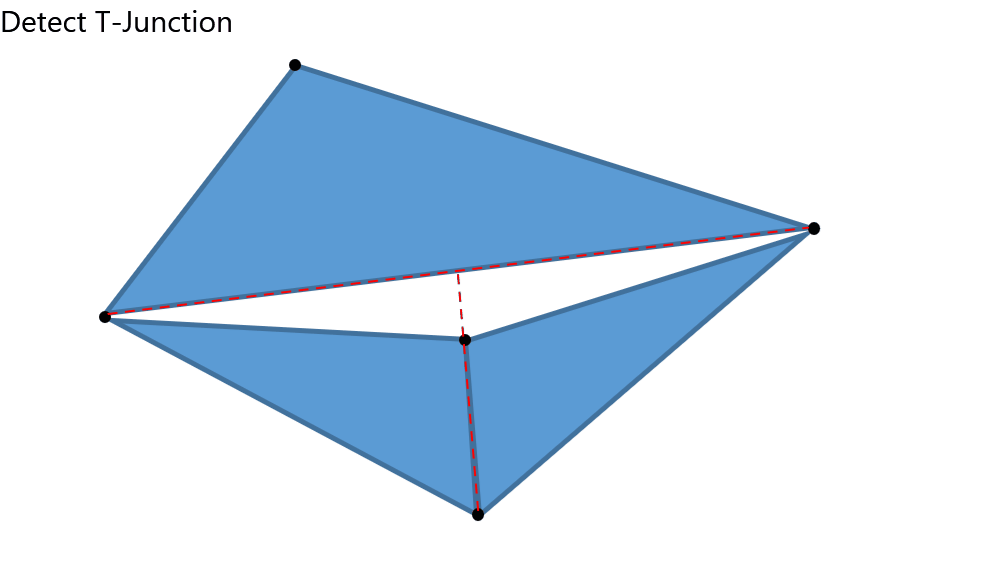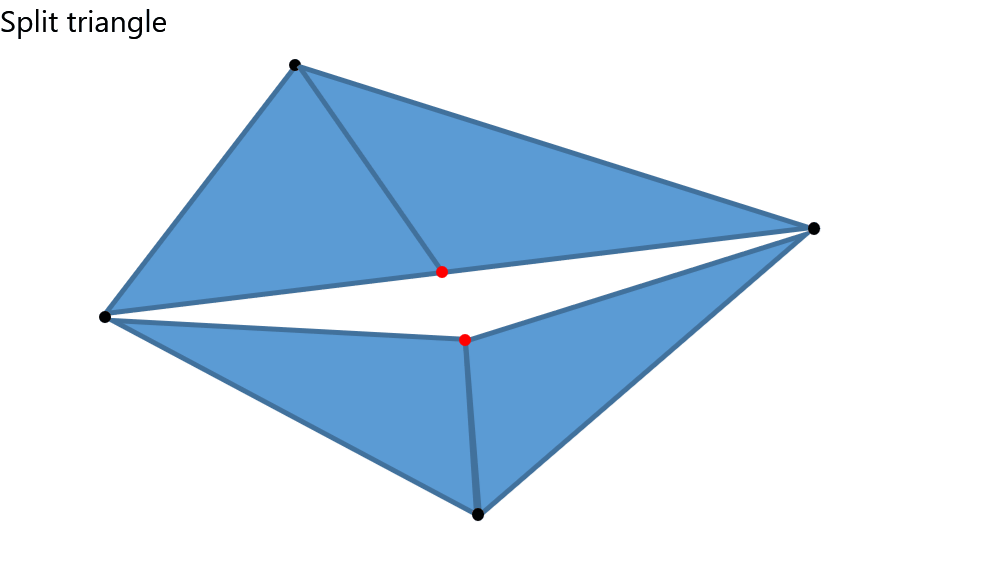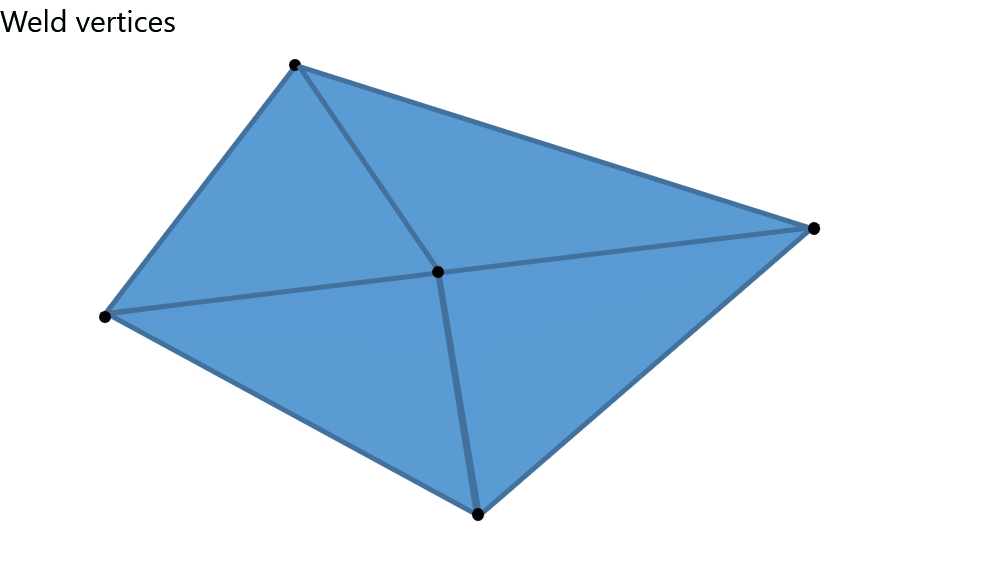
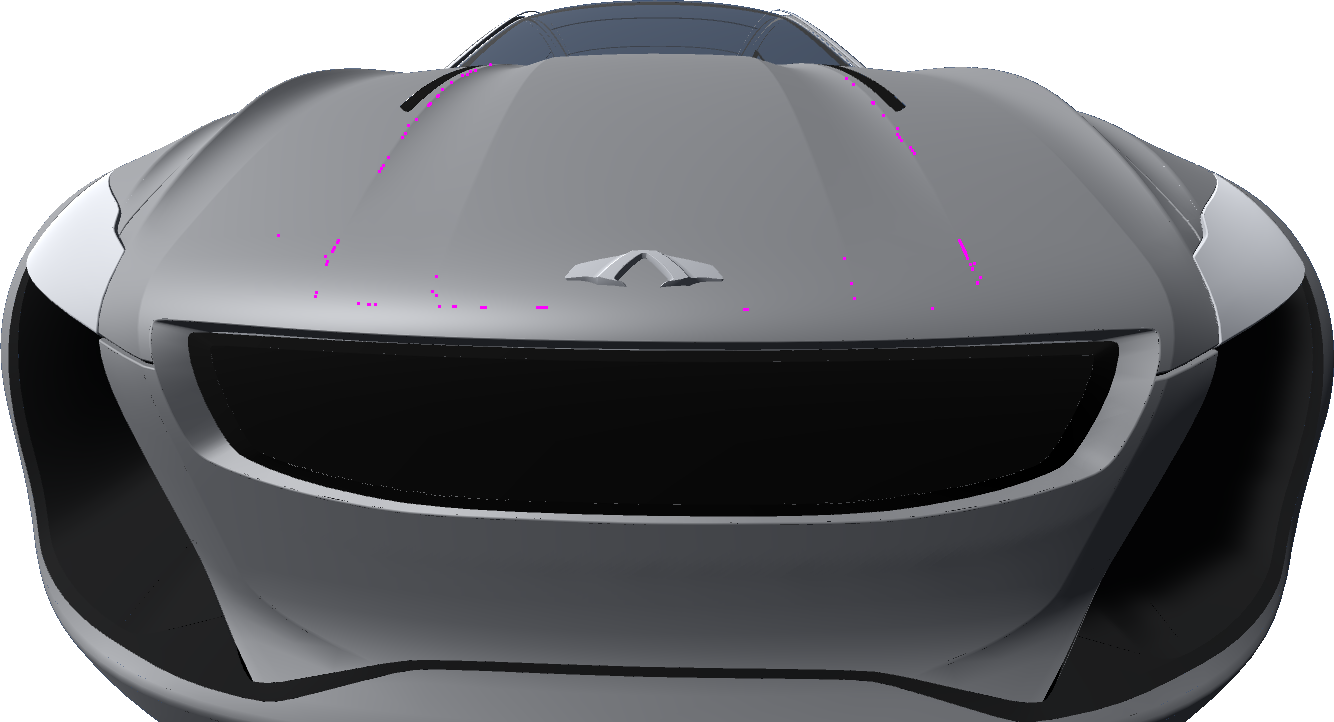 |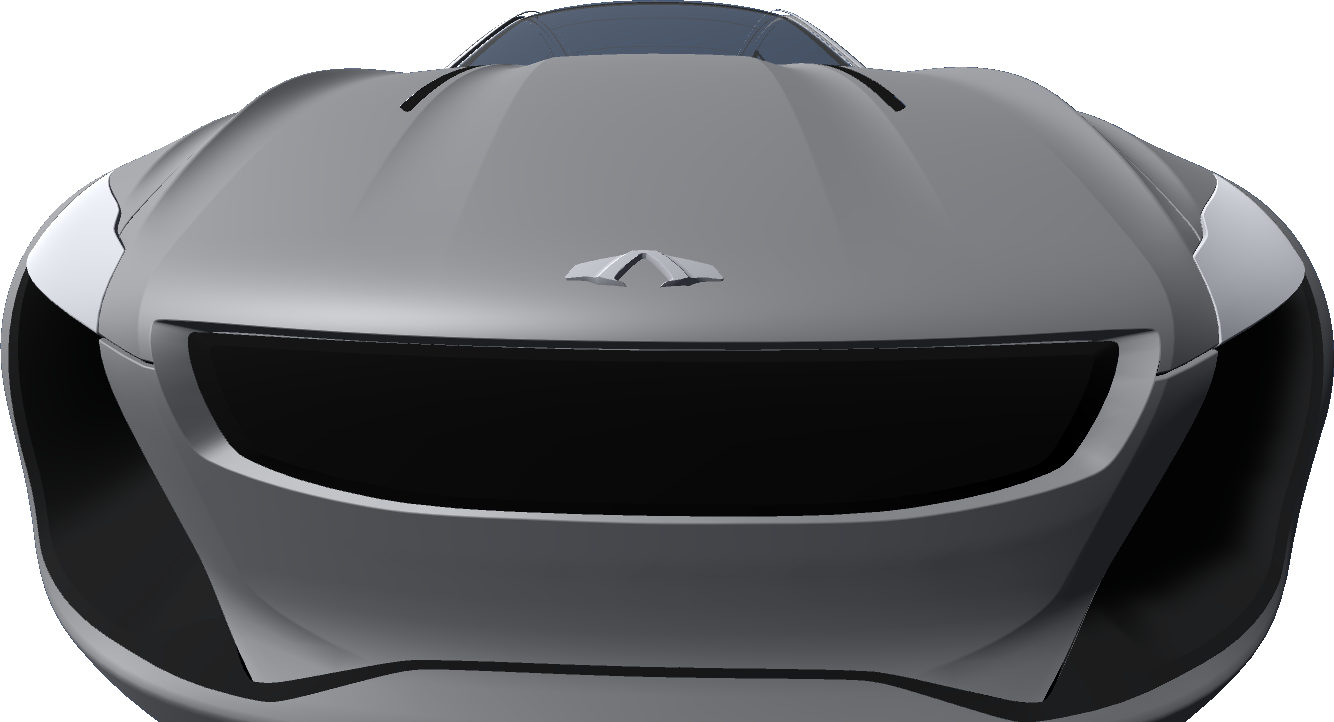  |
Non-manifold edges
This illustration shows the difference between manifold edges and non-manifold edges: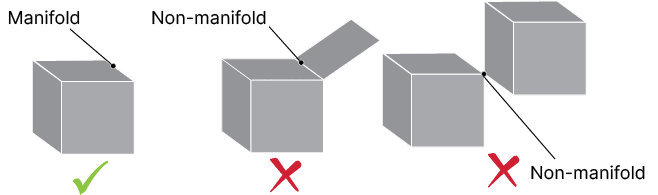
- Irregular mesh
- An unnecessarily high polygon count on curves
- Other issues in subsequent processing that requires manifold topology, for example decimation
Face orientation
This feature flips adjacent faces consistently to the same side, in two steps:- Crack Möbius strips of polygons
- Flip the polygons of a strip consistently to the same side
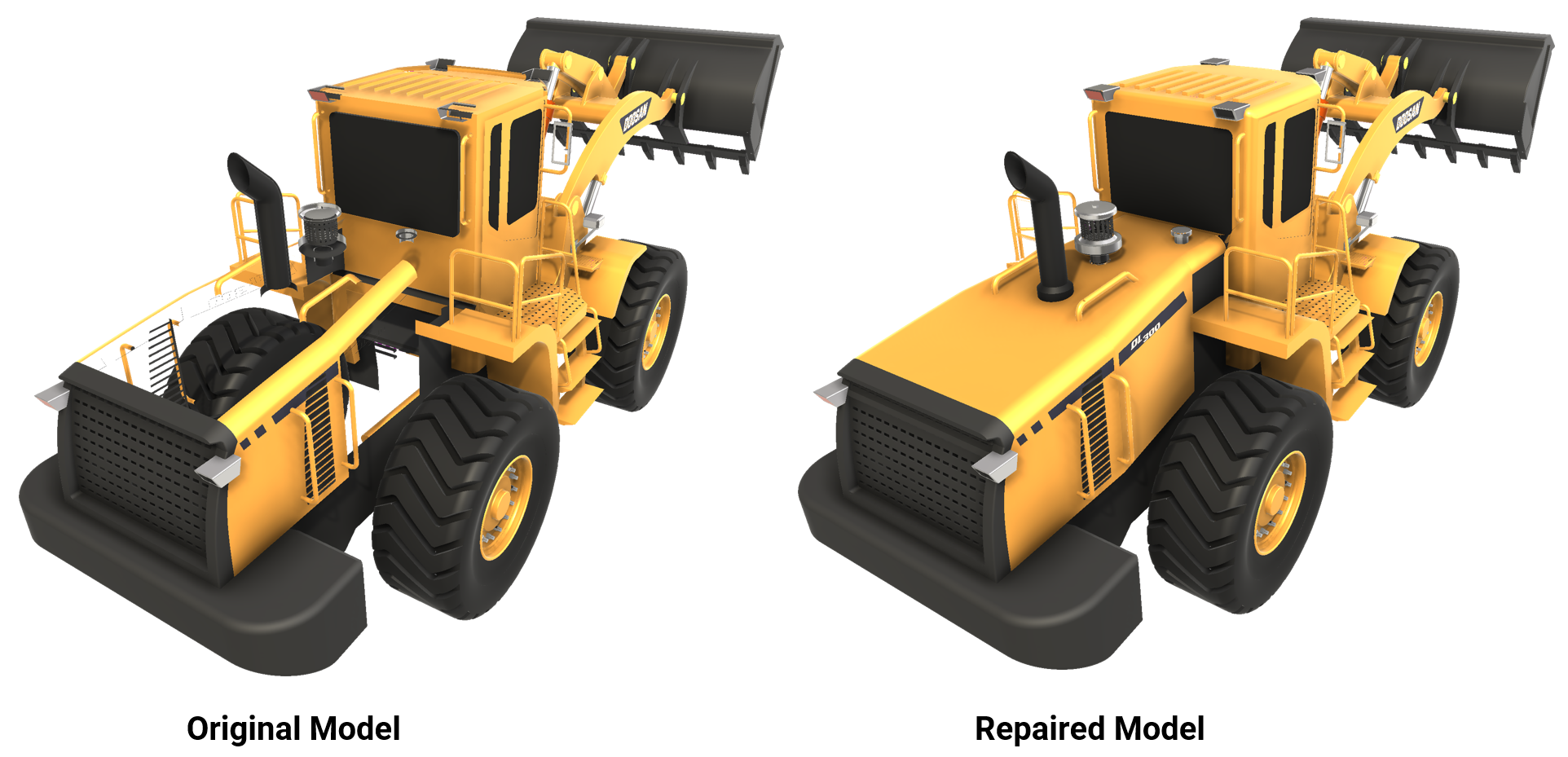
We recommend that you disable this parameter if the face orientation is correct.