コードの統合
Implement Remote Config in your game code using the RemoteConfig API.
読み終わるまでの所要時間 4 分最終更新 3ヶ月前
RemoteConfigUnity.Servicesカスタム属性の実装
Game Overrides の条件 にカスタム属性を提供するには、以下のstruct- アプリケーションが独自のトラッキング方法を使用している場合、構造体を使用し、
Deliveryメソッドでカスタムプレイヤー ID 属性を提供します。開発者が定義した属性がない場合、Remote Config は ID を自動生成します。SetCustomUserID - 構造体を使用して、カスタム user カテゴリ属性を提供します。
userAttributes - 構造体を使用して、カスタム app カテゴリ属性を提供します。
appAttributes - 構造体を使用して、ペイロードを削減するために、カスタム filter カテゴリ属性を提供します。
filterAttributes
using UnityEngine;using Unity.Services.RemoteConfig;using Unity.Services.Authentication;using Unity.Services.Core;using System.Threading.Tasks;public class RemoteConfigExample : MonoBehaviour { public struct userAttributes { // Optionally declare variables for any custom user attributes: public bool expansionFlag; } public struct appAttributes { // Optionally declare variables for any custom app attributes: public int level; public int score; public string appVersion; } public struct filterAttributes { // Optionally declare variables for attributes to filter on any of following parameters: public string[] key; public string[] type; public string[] schemaId; } // Optionally declare a unique assignmentId if you need it for tracking: public string assignmentId; // Declare any Settings variables you’ll want to configure remotely: public int enemyVolume; public float enemyHealth; public float enemyDamage; // The Remote Config package depends on Unity's authentication and core services. // These dependencies require a small amount of user code for proper configuration. async Task InitializeRemoteConfigAsync() { // initialize handlers for unity game services await UnityServices.InitializeAsync(); // options can be passed in the initializer, e.g if you want to set AnalyticsUserId or an EnvironmentName use the lines from below: // var options = new InitializationOptions() // .SetEnvironmentName("testing") // .SetAnalyticsUserId("test-user-id-12345"); // await UnityServices.InitializeAsync(options); // remote config requires authentication for managing environment information if (!AuthenticationService.Instance.IsSignedIn) { await AuthenticationService.Instance.SignInAnonymouslyAsync(); } } async Task Awake () { // In this example, you will fetch configuration settings on Awake. } // Create a function to set your variables to their keyed values: void ApplyRemoteConfig (ConfigResponse configResponse) { // You will implement this in the final step. }}
ランタイムでの設定の取得と適用
次に、Remote Config サポート関数を実装し、ランタイムに呼び出してサービスから Key-Value ペアを取得し、それらを適切な変数にマップします。 Remote Config サービスは、ランタイムでの設定の取得と適用を処理するためのRemoteConfigService.InstanceApplyRemoteConfigApplyRemoteConfigConfigResponseRemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig// Retrieve and apply the current key-value pairs from the service on Awake:async Task Awake () { // initialize Unity's authentication and core services, however check for internet connection // in order to fail gracefully without throwing exception if connection does not exist if (Utilities.CheckForInternetConnection()) { await InitializeRemoteConfigAsync(); } // Add a listener to apply settings when successfully retrieved: RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchCompleted += ApplyRemoteConfig; // you can set the user’s unique ID: // RemoteConfigService.Instance.SetCustomUserID("some-user-id"); // you can set the environment ID: // RemoteConfigService.Instance.SetEnvironmentID("an-env-id"); // Fetch configuration settings from the remote service, they must be called with the attributes structs (empty or with custom attributes) to initiate the WebRequest. await RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigsAsync(new userAttributes(), new appAttributes()); // Example on how to fetch configuration settings using filter attributes: // var fAttributes = new filterAttributes(); // fAttributes.key = new string[] { "sword","cannon" }; // RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigs(new userAttributes(), new appAttributes(), fAttributes); // Example on how to fetch configuration settings if you have dedicated configType: // var configType = "specialConfigType"; // Fetch configs of that configType // RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigs(configType, new userAttributes(), new appAttributes()); // Configuration can be fetched with both configType and fAttributes passed // RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigs(configType, new userAttributes(), new appAttributes(), fAttributes); // All examples from above will also work asynchronously, returning Task<RuntimeConfig> // await RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigsAsync(new userAttributes(), new appAttributes()); // await RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigsAsync(new userAttributes(), new appAttributes(), fAttributes); // await RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigsAsync(configType, new userAttributes(), new appAttributes()); // await RemoteConfigService.Instance.FetchConfigsAsync(configType, new userAttributes(), new appAttributes(), fAttributes);}void ApplyRemoteConfig (ConfigResponse configResponse) { // Conditionally update settings, depending on the response's origin: switch (configResponse.requestOrigin) { case ConfigOrigin.Default: Debug.Log ("No settings loaded this session and no local cache file exists; using default values."); break; case ConfigOrigin.Cached: Debug.Log ("No settings loaded this session; using cached values from a previous session."); break; case ConfigOrigin.Remote: Debug.Log ("New settings loaded this session; update values accordingly."); break; } enemyVolume = RemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.GetInt("enemyVolume"); enemyHealth = RemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.GetInt("enemyHealth"); enemyDamage = RemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.GetFloat("enemyDamage"); assignmentId = RemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.assignmentId; // These calls could also be used with the 2nd optional arg to provide a default value, e.g: // enemyVolume = RemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.GetInt("enemyVolume", 100);}
特定の設定タイプを使用した設定へのアクセス
対応する設定タイプのすべての設定は、キャッシュに正しく格納されます。これには、以下のように設定タイプを渡すことでアクセスできます。RemoteConfigService.Instance.GetConfig("settings");RemoteConfigService.Instance.GetConfig("specialConfigType");
メタデータパラメーター
リクエスト時に毎回バックエンドで割り当てイベントが作成されます。 そのリクエストへの応答内で、configsmetadata
- 各割り当てイベントで が作成され、イベントと最終的なユーザーのセグメント化を追跡するために使用されます。
assignmentId - は割り当てが行われた環境を表します。
environmentId - は割り当て時に作成され、その特定の割り当ての一意のシグネチャを表します。
configAssignmentHash
configAssignmentHashappConfig使用したいRemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.configAssignmentHash
configAssignmentHashSetConfigAssignmentHash()RemoteConfigService.Instance.SetConfigAssignmentHash("4d1064c5198a26f073fe8301da3fc5ead35d20d1");
configAssignmentHashconfigAssignmentHashconfigAssignmentHashconfigAssignmentHashその他の考慮事項
オブジェクトを上書きするために JSON 型の設定を使用する
例えば、以下のようにコードにCubeInfoJSON エディターモーダルは、以下のタイプの JSON 変換をサポートしています。[System.Serializable]public class CubeInfo{ public float rotateX = 10f; public float rotateY = 10f; public float rotateZ = 10f; public float rotSpeed = 1.0f; public Color color = Color.white;}
- テキストアセット
- スクリプタブルオブジェクト
- ゲームオブジェクトにアタッチされているカスタムスクリプト
CubeInfo
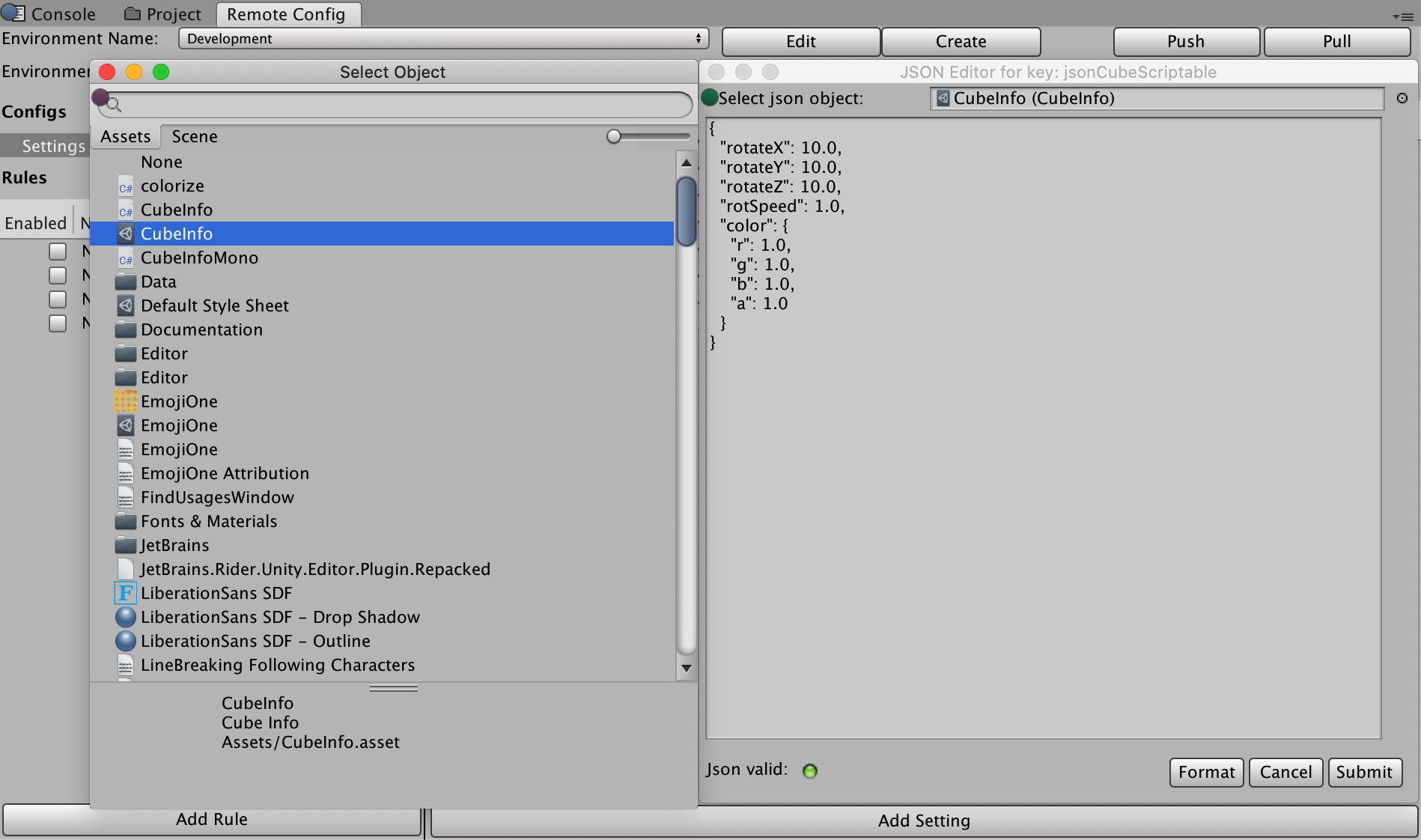

case ConfigOrigin.Remote:var jsonCubeString = RemoteConfigService.Instance.appConfig.GetJson("jsonCubeString");JsonUtility.FromJsonOverwrite(jsonCubeString, CubeInfo);
セキュリティ
Unity が Remote Config データをダウンロードするウェブサービスは読み取り専用ですが、安全ではありません。第三者が Remote Config データを参照する可能性があります。設定に機密情報や秘密情報を保存しないようにしてください。同様に、保存された設定ファイルはエンドユーザーに読み取りおよび変更される可能性があります (ただし、Remote Config は使用可能なインターネット接続で次にセッションが開始されたときに変更をすべて上書きします)。プラットフォームサポート
Remote Config Runtime の最新バージョンは、以下のプラットフォームでテストされています。 デスクトップ:- Windows (PC)
- Mac
- Linux スタンドアロン
- iOS
- Android